Personal computers should be compatible with new hardware even several years after they were purchased. This is necessary so that you can subsequently upgrade.
Often, PC component manufacturers offer users to update the BIOS on their own to keep the computer up-to-date and compatible with the new hardware. With this operation, you can easily install a processor that was not yet released when you bought the motherboard. In this case, your system will immediately recognize it and will function correctly. How is this possible?
Stand-alone system: BIOS with battery
BIOS (Basic Input / Output System) is the heart of software and an essential element of any PC. It acts as an intermediary between the computer components and the operating system: without the BIOS, the latter would not be able to communicate with the hardware and control it. When you turn on the computer, long before the OS logo appears on the screen, the BIOS always starts first. It determines which components are installed in the PC, initializes them and provides all the information to boot the system. The BIOS itself is located on a special flash memory chip on the motherboard of the computer, and the contents of the memory are retained even in the absence of power supply. This is possible due to the presence of a separate battery that is responsible for the BIOS.
We will answer the most important questions about BIOS and possible updates. Who needs to upgrade it? How do I know which motherboard is installed in my computer and which BIOS version it is using? If there is a need to update the latter, how to carry out this procedure? And what if you run into problems? It should be noted right away that not every PC needs an update: if the system is stable, it makes no sense. But those who are planning a computer upgrade and a thorough replacement of hardware or want to improve system performance cannot do without flashing the BIOS.
BIOS Setup: Additional Features After Update

BIOS Setup. The main BIOS menu consists of many sections. Any motherboard supports only a limited number of processor models, but by updating the BIOS, this list can be significantly expanded to include more modern chips. A prerequisite for this is the compatibility of the central processor with the motherboard connector. Problems can only arise with very old motherboards: the older they get, the less likely it is that a BIOS update makes sense.
It is also worth noting that when flashing it, it is far from always possible to achieve an increase in system performance. However, BIOS accessibility features and functions, such as overclocking the CPU, are often not available until after an update. Likewise, only after flashing the BIOS, new processors are correctly recognized and operate at the desired clock frequency. In addition, the latest BIOS versions provide useful features that enhance the customization options for your system. A typical example is Turbo Boost support for Intel processors. But before updating, you need to make some preparations: in addition to the motherboard identifier, you need to find out the number of the installed BIOS version. The free utility CPU-Z will help you with this.
CPU-Z: getting useful information

CPU-Z will provide the most detailed information about the components. This appendix provides information about the installed processor: name, manufacturer, core voltage, information about the cache memory, sets of supported instructions and other data. Also, CPU-Z can determine if the processor has been overclocked or is running at the factory frequency. After starting the utility, on the "Motherboard" tab, you can find out all the information about the manufacturer, the name of the model and chipset, as well as the current BIOS version. Compare this data with the parameters of your motherboard indicated on the manufacturer's official website. If the digit in CPU-Z matches the most recent BIOS version number, no flashing is required. If there is a more recent version on the site, download the required archive. It usually contains an executable file with an exe extension that is used to update the BIOS (for example, amiflash.exe, awdflash.exe, etc.), and a file with the BIOS code in BIN or ROM format. Flashing methods may vary depending on the motherboard manufacturer. Most developers offer their own utilities that allow you to update the BIOS directly from the Windows environment. However, for security reasons, we recommend using a more reliable method.
DOS: the best environment for updating BIOS
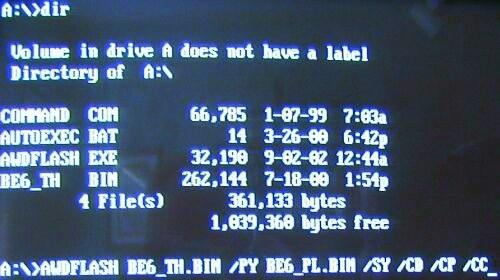
DOS - the safest environment for flashing BIOS With the least risk, flashing is done using a bootable floppy disk, disk or flash drive in DOS mode. The first of these media can be created, for example, in Windows Explorer: just right-click on the shortcut of the floppy drive and select "Format", activate the "Create MS-DOS boot diskette" option in the context menu and specify the path to the downloaded BIOS files.
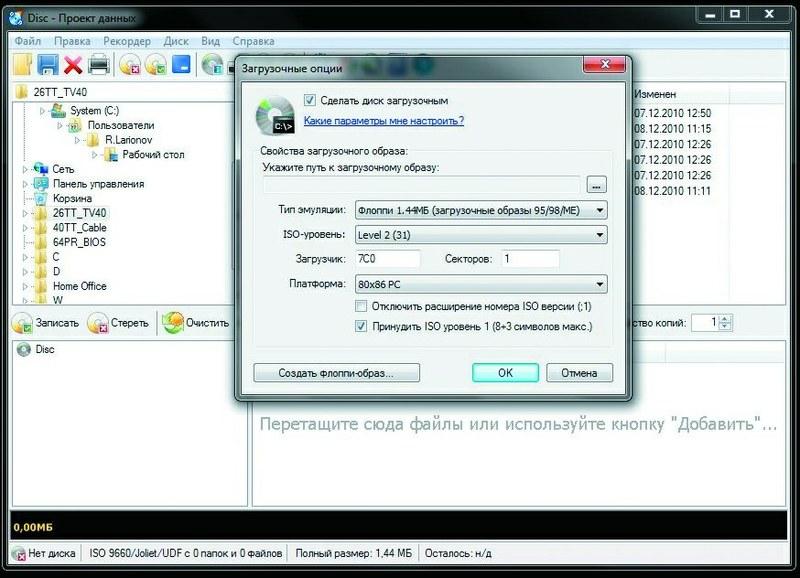
CDBurnerXP is a free disc burning program that emulates a bootable floppy disk for flashing BIOS. A bootable CD can be created using almost any free disc burning program, such as the CDBurnerXP utility.
You will need a boot image named boot.ima, which can be found on the CDBurnerXP website or on our DVD. It should be opened using the Ultra ISO program, drag the files with your BIOS code into the list that opens and save. After that, start the CDBurnerXP program, select the "Data Disc" recording mode and click OK. The main program window will open. Make the disk bootable: select “Disk | Boot options ", in the window that opens, check the box" Make disk bootable "and set the path to the saved boot image, specifying the type of emulation" Floppy 1.44 MB ". Burn a CD by clicking on the burn button, then restart your computer and point to your drive in the start menu. The computer will boot into DOS with a command prompt with the A:> directory open. If you enter "dir / w", you can view the contents of the floppy or disk. BIOS flashing can be done from the command line. Sometimes the BIOS update does not start automatically - in this case, run the dir command and run the file with the BAT extension (for example, update.bat). After successful flashing, remove the disc and restart your computer.
BIOS flavors: AMI, Phoenix and Award
As a rule, each motherboard model requires its own BIOS, since it must take into account the peculiarities of the used chipset and peripheral equipment. However, it is unprofitable for board creators to spend time and money on the full cycle of developing their own BIOS, so obtaining them usually consists of two stages. The BIOS manufacturer (the most famous companies are AMI, Award and Phoenix) is developing a basic version, which implements all the functions that do not depend on the features of a particular chipset. The creator of the motherboard, independently or together with him, improves the basic version, taking into account the peculiarities of a particular product. At the same time, for the same model, the BIOS code may change several times after the motherboard is released - for example, to fix found errors or add support for new devices.
Thus, the term "BIOS version" can be used to refer to a version of the BIOS base code released by a specialized company. For example, AwardBIOS 6.0 is the sixth BIOS version from Award, modifications of which are used in many motherboards. For each motherboard model, the source code is being finalized taking into account the peculiarities of the chipset and peripheral devices. Sometimes you can find BIOS versions entirely created by manufacturers of motherboards or laptops - Intel, IBM, Compaq, Toshiba, Dell and some other well-known companies. In terms of operation and interface, they are not much different from BIOS produced by Award, AMI or Phoenix, so it's not very difficult to deal with them.
If an AMI BIOS is installed on the motherboard, then the “amiflash.exe BIOS.bin” command is used to update it, and the word BIOS must be replaced with the name of the file with the code. After executing the command, a window will open showing the progress of the BIOS update. During flashing, under no circumstances should you turn off the computer or disconnect the power supply, as this may cause irreparable damage to the system. Once the process is complete, the program will automatically restart the PC. Remove the boot floppy or disc from the drive and boot Windows. Using the CPU-Z utility, you can check if a new BIOS version has been installed. However, flashing does not always go smoothly. But even if there are some problems and after updating the BIOS your computer no longer boots, this does not mean that it cannot be saved.
If the warranty period for your PC has not expired and you have dealt with programs and firmware from official developers, you can file a claim with the manufacturer.
However, the use of modified BIOS files from third-party vendors that promise better performance or more overclocking potential are not covered under warranty. Alternatively, you can use the paid services of firms specializing in recovering motherboards with BIOS errors. In some situations, creating a floppy disk with a firmware program and a file with a BIOS code on another, working computer helps. In the case of BIOS from Phoenix or Award companies, you need to create a file named autoexec.bat on a floppy disk. For this, use the standard Windows program - Notepad. The file should contain the following line: awdflash.exe BIOS_DATA / py / sn Replace BIOS_DATA with the name of the BIOS code file (including the extension - usually bin or rom).
The / py and / sn keys are needed to perform a flashing without further user intervention.
Advice.
If an AMI BIOS is installed on the motherboard, it is enough to save the file with the BIOS code on a floppy disk and rename it to amiboot.rom.
Insert the floppy disk and press the "Ctrl + Home" key combination during boot.
However, this solution helps only in 10–20% of all cases, since if the BIOS is damaged, it is often impossible to access the drive.
Last way of salvation: when all else fails

A damaged BIOS chip can be restored using another, working computer. If someone you know has the same motherboard model, you can restore your BIOS using another computer. Boot a working PC in DOS mode and prepare a floppy disk with all the data necessary for the firmware. Directly while the computer is running, using tweezers, carefully remove the BIOS chip from the motherboard and insert your damaged one. This requires utmost care as the PC is turned on.
Now start the flashing process from the floppy disk. This will update your faulty BIOS chip on your working motherboard programmatically. Then turn off your computer and swap components again. If everything was done correctly, the PC with a working BIOS will boot again.
However, it should be noted that updating the BIOS and correcting errors in all the described ways are performed solely at your own risk.
If the computer does not start

After updating the BIOS, your PC stopped turning on and you can't even enter BIOS settings? Disconnect the computer from the mains by unplugging the power plug.
Open the case of the system unit and touch a flat metal surface on the inside with your hand to discharge static electricity.
Find the battery on the motherboard. Remember how it is installed (as a rule, "+" is at the top). Remove it by pushing the metal contact to the side. Wait a minute and reinstall the battery. After turning on the computer, the BIOS settings will be reset to the factory defaults.
If you are not sure about the newly set parameters, activate the “Load Setup Defaults” function and exit the BIOS with saving.
The PC must be constantly updated. And this applies not only to hardware, operating system and applications. But it is advisable to do this only when a serious need arises.
If the machine works in normal mode without glitches and errors, then there is simply no need to update to the latest BIOS version. Since this procedure is extremely unsafe.
Why update
The new firmware for the device in question requires:
- new installed device is not supported;
- when there is a conflict with any application that needs to be installed on a personal computer;
- when it is necessary to increase the performance of the PC;
- if the outdated firmware is damaged.
Most often, an update is required due to the installation of new equipment - a processor, a hard disk. Much less often - video cards, RAM. This need arises from a conflict between hardware and firmware. Very often old BIOSes simply do not see large hard drives. This situation is corrected in most cases by updating.
Some applications do not support working with certain BIOSes and their programs. In most cases, this situation can be resolved by updating the version. Sometimes it is required to run some professional applications.
Often, old firmwares simply do not allow you to overclock the processor in various ways. If it is necessary to change the frequency of the CPU upward or apply a higher voltage to it, it is necessary to update the BIOS. This usually provides ample opportunities for manipulating various kinds of parameters of the central processor and other devices.
Sometimes the PC starts giving errors just like that, for no apparent reason. Bios is often the culprit. It is the installation of a new program in BIOS that allows solving problems of this kind in many cases.
Video: reflash BIOS
Current version
There are several ways to determine the BIOS version:
- before starting the OS boot;
- by means of the operating system;
- using third-party software.
In order not to waste time on performing any unnecessary actions, the owner of the PC can simply look at the labeling of the software of the device in question even before starting Windows.
To do this, you need to perform in a strict order of actions:
- turn on the PC;
- wait for the corresponding icon to appear ("American Megatrends", "Energy" and others);
- click on the button called "Pause Break".

This key allows you to stop loading the personal computer at any stage. Wait until a table or a list of characteristics appears on the monitor. The user needs to find the inscription "Bios Revision" or "Bios Version". There must be a combination of numbers next to one of these phrases. It is these numbers that indicate the version of the Bios used.
You can also find out the labeling of the software of the PC component in question by simply going into its settings.
To do this, you need to do the following:
- turn on the computer;
- until the image appears, press the "Delete" key several times;
- in the section called "Main" find item "Information" -> "Version".

The easiest and safest way to find out the version is to use the item in the Start button called Run.
It is necessary to carry out the following actions:
- open "Run";
- in the field that appears, enter "msinfo32";
- click on "Enter" or just click on "Ok".
This will open a standard Windows operating system component. It contains all the information about the system, including the Bios firmware information.

How to update Bios on a computer
There are three ways to update the software for the device in question:
- in MS-DOS mode;
- in Microsoft Windows directly;
- without logging into Windows and MS-DOS.
Each method has both advantages and disadvantages.
Where to get the update
To update the Bios, you first need to find the correct application for this PC component. It is best to download it from the official website of the motherboard or Bios manufacturer. The surest way to find out the model and name of the manufacturer of computer components is to visually inspect the motherboard itself, the chip of the updated device located on it.
You can also use any specialized program in order to find out the marking of the firmware and the name of the manufacturer. Everest is best suited for this. The most important advantage of this application over its counterparts is that it offers the user links to the official websites of the manufacturer, where you can find everything you need.

Another source of new firmware versions can be various unofficial sites on the Internet. But the likelihood of downloading counterfeit software with a virus or simply not working, which can damage your PC, is very high. Therefore, it is highly discouraged to use applications from unreliable sources.
Making a backup
Before performing any actions that make changes to the firmware, you must make a backup copy of it. This will avoid all sorts of problems when an error occurs that makes the hardware inoperable. The backup copy must be saved to an external medium (USB-disk, flash drive, floppy disk) in order to avoid the need to extract it from the hard disk.
The easiest way to make a copy of the software to be updated is using an application called EZ Flash (used by ASUS).
The copying process consists of the following main steps:
- making a bootable USB flash drive with the MS-DOS operating system;
- by inserting the USB flash drive into the port, you need to restart the PC;
- after pressing the "Delete" key during loading, you should find the "Tool" tab;
- choose Asus EZ 2 Utility;
- press the "F2" key and enter the name of the backup.
After completing all of the above operations, all data necessary for recovery will be saved on the selected media. If necessary, they can be easily used.

Installation
The easiest way is to install new software on the considered component of a personal computer directly in the Windows operating system.
To do this, follow these steps:
- download a special update program for a specific motherboard model;
- run the executable file.
Most manufacturers have their own update application. That is why it is necessary to use only files downloaded from official resources. For example, ASUS has an application for performing this action called ASUSUpdate. It is installed like the most common application, the menu is intuitive, even if it is in English.

Some manufacturers provide for updating their products without logging into the OS. In the ROM of the equipment, special means are already embedded in the update. For example, the ASRock Instant Flash utility can independently perform all the necessary actions in a matter of minutes. You just need to press "F6" - it will scan all available sources of information.
Reset system settings
There are two ways to reset the system settings:
- software;
- hardware.
To use the first method, you must:

To perform a hardware reset, you must use a special jumper or remove the battery from the special connector for at least 30 minutes. After performing the necessary actions, a reboot is performed.
Possible problems
When installing new firmware versions, various kinds of errors may occur:
- version mismatch;
- data writing error.
The most common problem is the use of inappropriate files for the update implementation. If this type of problem occurs, you must use a backup to restore the system to its original state. If an error occurs in writing data, then you should do the same - reset the settings to standard.
Video: update the BIOS
When carrying out an operation of this type, it is necessary to make sure that the applied voltage is stable. If the electrical current is cut off suddenly, there is a high probability of severe damage to the updated component. Which is unacceptable.
It is important to only use firmware from trusted sources. Since there is always a possibility of the presence of bookmarks or viruses in the extraneous data. All of these can damage your computer. It is also worth checking the health of the button cell battery inside the system unit.
Many users do not understand why they need to update Bios. It is necessary to perform this operation only in extreme cases, when it is simply not possible to resolve any conflict in an alternative way. The procedure should be carried out as carefully as possible in order to avoid damage.
At the end of 2016, Intel announced the release of the processor Kaby lake... New chip like its predecessor Skylake, uses the same 14-nanometer process technology, but it was not without optimization. The innovations have added performance to the chip, which surpasses the power of the 6th generation processor in Intel's "family". This naturally explains the consumer hype around Intel 7th generation processors. But what about bios who wants to upgrade? Let's talk about this.
And the difference is this: a comparison of Skylake and Kaby Lake
If you work with 4K content a lot, then buying a Kaby Lake processor is a smart investment... The new generation chips support HEVC. They delegate the encoding / decoding of UHD video format to the video card, and do not use their own kernels. Result - noticeable improvement in video quality and reduced battery consumption. Moreover, among the possibilities of processors is to direct their power to solving problems that await, while the tendency remains less energy consumption... 3D is getting better too. The picture quality is superior to that previously provided by 6th generation processors. The gameplay promises to be bright and detailed.
In addition, it is worth noting the pleasant updates - increase clock frequency, improvements turbo mode, support new formats (2nd generation USB 3.1, HDCP 2.2).

BIOS firmware update to support Kaby Lake
Are you planning or have already bought a Cabi Lake processor, but it does not work on your machine? The situation will be saved by the BIOS firmware, of course, provided that latest version of BIOS is designed to solve this problem. Intel insists to carry out a BIOS update for PCs that do not need it, not desirable.
To ensure the operation of the Intel 7th generation processor, owners of motherboards with Z170, H170, B150, H110 chipsets can update BIOS... Firmware update is in progress extremely simple, but safer contact the service. The fact is that in the process difficulties often arise, with which it is unrealistic for an amateur to cope.
The transition from the 6th generation is carried out in several ways, and it all depends on will the payment work without updating. If not, then for firmware need Skylake... If the motherboard supports the technology Q-Flash Plus, then it will be possible to update from a USB flash drive and without a processor. In other cases - need a programmer, and in addition, the desoldering of the BIOS memory chip. Agree hard and resource-intensive.
BIOS updates - required condition even for those motherboards that have received support for 7th generation chips (for example, Intel H110 / B150). Although there have been platforms on the market for some time that allow the use of upgraded CPUs, nobody guarantees that when you buy, you will not get a device whose BIOS version does not support Kaby Lake. In such a situation, you will also have to to apply for help from Skylake or go to the service center.
What does the KomPom service center offer?
The ComPom service updates the BIOS firmware to support the 7th generation of Intel processors without loss of guarantee... At our disposal modern equipment which allows quickly and qualitatively make the transition from 6th generation to Kaby Lake.
Motherboard models with which we work:
- Afox H110
- ASRock H110
- Asus H110
- Biostar H110
- EliteGroup (ECS) H110
- Gigabyte GA-H110
- MSI H110
- ASRock H170
- Asus H170
- Gigabyte GA-H170
- MSI H170
- ASRock B150
- Gigabyte GA-B150
- MSI B150
- Asus B150
- ASRock Z170
- Asus Z170
- EVGA Z170
- Gigabyte GA-Z170
- MSI Z170
- Asus Q170 etc ..
The most common reason customers ask for an upgrade is because of the Intel Pentium G4560 processor in 100th motherboards. And we are happy to solve the problem of compatibility of 100-series chipsets with 7th generation processors.
The master performs the firmware not through the operating system, where there is a risk of failure of the bios microcircuit. Our way - updating the BIOS firmware of the motherboard using the programmer... The firmware process takes on average 60 minutes!
We do not solder the BIOS chip!
Pleasant bonus for our clients - provision of a guarantee for all types of services.
Any computer hardware and software, as you know, becomes obsolete over time and ceases to meet current requirements. This applies equally to primary BIOS / UEFI systems, the software of which is integrated into a special chip on the motherboard. When installing new hardware ("hardware"), BIOS flashing may sometimes be required. On a laptop, on a stationary computer terminal, such a procedure will be performed, it does not matter. The technology is almost always the same. Some users unfamiliar with the basics of such techniques believe (and not without reason) that this process is unsafe and difficult. If one can agree with the first statement, then one can argue about the second. In fact, flashing the BIOS of a motherboard is not so troublesome. But for the correct conduct of such a procedure, special attention should be paid to some important details and nuances, which depends on the manufacturer of the motherboard and the programs and methods used for flashing.
What is BIOS flashing for?
In general, if it is not planned, and the whole system is working stably, there is basically no point in updating the BIOS version.
But when new hardware is installed on the computer, which may not be supported by the primary system only because of its obsolescence (the BIOS simply does not recognize the device), flashing the BIOS becomes an urgent problem. Although many users find this process difficult, any person who works with a computer will be able to perform these steps on their own. It will take no more than 10 minutes.
Flashing the motherboard BIOS: prerequisites
To get started, pay attention to a few prerequisites, failure to comply with which can lead to disastrous consequences.
You should download files and programs for updating primary systems only from the official resources of motherboard manufacturers. If an unofficial firmware is installed, no one will be able to guarantee that the process will be successful and the system will then work as expected.
The second thing to look out for is during the update. Make sure that there are no power surges or spontaneous disconnection of the computer or laptop from the mains, it is necessary in advance.
General rules for updating all firmware
BIOS flashing for almost all motherboard models implies the use of the same scheme:
For standard BIOS systems, DOS mode is used in most cases. However, for some BIOS versions, as well as for more modern UEFI systems, a special BIOS flashing program created by the motherboard manufacturer can be used, which can run even in Windows operating systems without the need to create bootable media.
How can I find out the motherboard modification and the current BIOS version?
The very first thing to do is to determine which motherboard model is installed in the computer system, as well as find out the version of the primary BIOS system (perhaps it is currently up-to-date and does not need updating).

You can view information about the board and BIOS version in the section called from the Run console using the msinfo32 command.

For the motherboard, you can also use specialized utilities like CPU-Z (formerly Everest). For a device determined in this way, you need to find the latest firmware on the manufacturer's website and save the files on your hard drive.
Preparing bootable media (general methodology)
In the case of using bootable media, when an update from under Windows is not provided, at the first stage it must be created. Plain recording of uploaded files will not work.

To simplify the work, you can use the Rufus utility, which is very easy to learn and creates a bootable USB flash drive in a couple of minutes. Almost nothing needs to be changed in the parameters. Only in the file system should you specify FAT32, and use MS-DOS mode in the write method, be sure to check the box opposite the line for creating bootable media. If this is not done, then upon rebooting the device will not be recognized as bootable. Then, to install the update, in some cases, it will be necessary to additionally copy the control program and the firmware file to the media.
Next, the process of updating the BIOS will be considered with examples for motherboards from several well-known manufacturers. Although in general they are very similar to each other, nevertheless, each of them has its own nuances. We assume that the priority has already been set in the BIOS settings.
ASUS
Re-flashing the BIOS "Asus" can be done in several ways. Among the preferred utilities, two programs are worth highlighting - AFUDOS and ASUSTeK EZ Flash 2.
When using the first utility, you should create a bootable media and make sure that it contains the afudos.exe program file and the firmware itself (for example, p4c800b.rom).

ASUS BIOS flashing is as follows. We boot from the USB stick. Since the media was recorded for DOS mode, the initial line C: \> will appear on a black screen, in which you need to write the / i p4c800b.rom command and press the enter key. Upon completion of the update, a reboot will occur, during which you just need to remove the media from the USB port to start the system from the hard disk.
Re-flashing the BIOS of the ASUS motherboard when using the second utility is somewhat different from the previous version.
Despite the fact that most of the firmwares on the official ASUS website have the .rom extension, sometimes CAB files can also be found. There is nothing wrong with that, since they are used for UEFI systems.

For the firmware, enter the UEFI settings on reboot, go to Advanced Mode (additional settings) and select the ASUSTeK EZ Flash 2 line in the Tool service (tools) section. which on the right will be shown the desired firmware file. We select it and twice agree with the warning (first to check the file, then to start the firmware process).
At the end of the process, a notification about the reboot will appear, and at the beginning of the restart, you will be prompted to carry out the initial configuration. Press F1 and set the required parameters. Otherwise, just exit the settings without saving the changes.
Gigabyte
BIOS flashing of Gigabyte-systems differs from other processes quite strongly. This is primarily due to the fact that an online update can be used to install the firmware. But first, let's look at using the Q-Flash utility, which is believed to be the best for updating firmware.

First, you should enter the BIOS settings and use the option to reset all settings Load Optimized default. After that, you need to save the changes, restart the computer and enter the BIOS settings again. Further, to launch the Q-Flash utility, press the F8 key, and the start is confirmed by pressing the Y and Enter keys. First, it is recommended to save the current version using the Save Bios option, after which you need to use Update Bios. Next, a request will follow to indicate the source from which you want to update. Select HDD 2.0 as the storage medium (this is how the flash drive is displayed in the settings). Then everything is as usual: we select the firmware file present on the media and agree with all the warnings.
For the Internet update, you can use the @BIOS utility specially developed by Gigabyte specialists, which runs in the Windows environment. In this case, it is strongly recommended to disable Hyper-Threading mode in the settings of the primary system, as well as deactivate antivirus and other resident applications to avoid errors or failures during the update process.
After starting the program, you can immediately save the current BIOS version by clicking the Save Current BIOS button, and then select the Internet Update online update mode, click Update New BIOS and specify one of the servers present in the list. After that, you will be prompted to indicate the model of the installed motherboard, and the program will automatically download all the necessary components and activate the update process.
MSI
MSI BIOS flashing, as in the case of ASUS, can be done either from under Windows or from under DOS. For DOS mode, a BIOS-MFLASH tool is used built into the BIOS. But the MSI Live Update 5 or 6 application can also be used as an initial control utility. It is notable for the fact that it can also update all installed MSI drivers, as well as reflash the BIOS of the corresponding graphics accelerators. Let's start with him.

In the main window, you just need to check the boxes on the necessary items. Select the MB BIOS component and press the scan button from the bottom (Scan). If a new firmware version is found, use the Download and Install button, after which the update process will start.

First, you will need to select the update environment. To simplify matters, check the In Windows mode item, in the next window, press the button to close all programs that appear in the list (Close all listed programs), press the Continue button (Next) and in the next window press the button to start the process.
For DOS mode, select it from the window of the running update process, after which we indicate the medium and agree to the destruction of all data present on it (the process will take no more than a minute, after which a message will be displayed about the successful creation of the bootable drive). When rebooting, all that remains is to follow the instructions of a kind of "Wizard".
In the case of an update using the built-in MFLASH mechanism, you will have to download the firmware manually, create a bootable media and perform the same actions in the BIOS as described above (the media and the firmware file are selected in the tools menu).
Acer
Re-flashing the BIOS of Acer systems is surprisingly much easier. You don't even need to create a bootable media, although you still have to format it to FAT32.

To install the update, a special utility called Insyde Flash is used, which is copied to removable media. At the same time, into the main program directory on a USB flash drive, you need to copy the firmware file downloaded from the official website with the extension .fd and corresponding not only to the motherboard, but also to the laptop model. Please note that the device must contain only one firmware file, otherwise the application will display a proposal to reflash only one of several. After starting the utility with the power on, you will be prompted to install the update immediately.
The second way is just as simple. First you need to completely turn off the laptop, unplug the power cord and wait until the power indicator stops blinking. Next, plug the cord into an outlet, insert the USB flash drive into the appropriate port, hold down the Fn and Esc keys and press the power button. As soon as the indicator starts flashing, release the pressed keys. After that, the reading of information from the drive will begin (this can be seen by the blinking of the LED on the device itself). At the end of the update process, the laptop will reboot itself.
Video cards
Since GeForce and Radeon are dominant in the video card market, BIOS flashing will be considered using their example.

At the initial stage, you need to download new firmware and control programs for your card on the manufacturer's website. If the system has several video cards, you need to leave only one during the update, inserting it into the PCI-Express slot.
For GeForce cards, the NVFlash program is used (two files), for Radeon cards, the ATIFlash utility (one file). Next, you need to create a bootable USB-drive for DOS-mode, and then copy the program and firmware files to it.
When starting from a flash drive, make sure that the card is single-processor, otherwise the proposed method will not work. For NVIDIA, use the nvflash --list command, for ATI use atiflash -i. If information on two cards is issued, then the adapter has two processors, and the proposed firmware method cannot be used (it is better to go to the manufacturer's website and find instructions there).
At the next stage, flashing the BIOS of the GeForce video card involves disabling protection. This is done with the nvflash -protectoff line.
Further, to start the BIOS update process for GeForce cards, use the command nvflash -4 -5 -6 newbios.rom (the name of the ROM file must correspond to the name of the loaded firmware), for Radeon cards - atiflash -p -f 0 newbios.rom. After that, we wait for the completion of the process and reboot the system in normal mode.
Brief summary
That's it for flashing primary I / O systems. Based on the foregoing, we can conclude that the best option is to install the update exclusively in DOS mode, although special utilities can be used to simplify the work. But they work only in the case of UEFI systems, and they are not suitable for standard BIOS versions. You need to be extremely careful with video cards, since incorrect installation of the update or the slightest violations during the flashing process can lead to the failure of the graphics adapter.
BIOS is a familiar abbreviation, the meaning of which is not familiar even to many sophisticated and experienced personal computer users. For most of them, it is associated with a gray-blue interface in the style of MS DOS or Windows 3.1, but many may not tell you about its functionality. Most of the knowledge of the average user, at best, is limited to the fact that BIOS is the system settings of a computer or something like that, because it is rather difficult to give an exact answer. This complexity is quite justified for itself - a personal computer is not easy for an ordinary person to understand when it comes to fast and productive work in any industry, and understanding the basic mechanisms of its functioning and, moreover, each of its components seems almost impossible - in practice, this knowledge borders on erudition and are not useful in most situations.
So, BIOS is an input / output system that stands between the hardware and software (together with the user) and allows the computer's resources to be used as intended. It has a read-only memory module that contains a number of data about the configuration of the equipment, including the time - all owners of old computers have faced battery replacement and could hear that it powers this particular component. An important feature of the BIOS is that the capabilities of other hardware located on the motherboard directly depend on its capabilities.
But for most PC users, all these technical issues are unimportant, and a practical need for those actions that they may face is necessary. These include, for example, replacing an outdated processor with a newer and more productive model: support by a motherboard at the software level directly depends on whether the BIOS is "friendly" with it. They may not add compatibility right away: if the slot for the processor (Socket) cannot be changed, then it is possible to create the necessary conditions for the functioning of a suitable hardware model, and the creators of motherboards for the most part take care of ensuring compatibility.
Why Flash BIOS?
As it became clear from the above, the BIOS ensures the joint operation of all components located on the motherboard. We are especially interested in the processor and RAM: their capabilities are developing at the most rapid rates and require the release of motherboard models with an appropriate speed. But this practice is not very profitable and the creators decided to leave a reserve for the future, leaving the user with the opportunity, within certain limits, to improve the compatibility of the motherboard with the hardware on his own. This was the reason for the appearance of the BIOS firmware procedure on personal computers, which allows you to get rid of many problems with it.
It is worth noting that the procedure is quite dangerous compared to other actions with a PC: if the light is turned off at the time of overwriting (rarely, but it happens), everything cannot be restored in any way and the motherboard can be put off somewhere else or simply thrown away. But in frequent cases, such a procedure is still necessary, it brings support not only for new components, but also tools for working with new equipment - old motherboard models that do not support flashing via USB devices got this opportunity thanks to the compatibility package included in the firmware. for similar equipment. The flexibility of a computer in its capabilities is invaluable, and in those cases when the firmware is still needed, do not be afraid of the high complexity of this process - if all procedures are performed correctly, the risk of harming the computer is minimal, and the process can often take only a few minutes, but it is worth talking about it in more detail.
Often, the manufacturer himself can recommend a flashing - this may be due to a number of shortcomings that they did not manage to notice and / or eliminate during the production phase. For many PC owners who own one of the new series of motherboards, this practice is not something unfamiliar - for objective reasons, this happens very often.
What motherboards need to be flashed with their BIOS?
An important feature of this whole story is the fact that there are still only three companies in the world that are engaged in the production of the software part of any input-output system. It will become intuitively clear to many that this increases the chances of each individual model for flashing, and in fact it turns out to be so: no matter what the manufacturer of your motherboard is, with a high degree of probability (which tends to a hundred percent), this procedure is possible for you. But it is worth adding that the same company is engaged in the delivery of updates and it is not in its commercial interests to invest large funds in increasing the performance and capabilities of old models - then there is simply no need to buy new ones.
The theoretical possibility of replacing the firmware is included in any BIOS - at the heart of the device is a memory module designed for approximately 1000 rewriting cycles. But the release of the firmware will be completely on the conscience of the motherboard manufacturer.

It is quite simple to check such a possibility: you just need to know the manufacturer and the model of your device and its model (if not, then welcome to the next section of the article). We go to its official website (that ASUS, that MSI, ASRock and others have their Russian-language versions) and follow the page dedicated to your version of the device. There, in one of the tabs, a category with all released firmware for this component will be available, as shown in the example of the official ASUS website below.

On the websites of other companies, the procedure is approximately the same - in the corresponding section all possible options for updating the BIOS will be offered, since in models from different manufacturers they differ in the process almost completely and the skill of flashing one component cannot guarantee knowledge of the subtleties in another - here it is worth carefully studying the proposed online for step-by-step guides, or ideally the manufacturer's own documentation. There are also many video flashing videos on the network: there are relatively few motherboard models, but out of those hundreds or thousands of users who have encountered a problem, at least one decided to record a video - all you need to do is search on video hosting sites. Viewing the process from the outside will deprive the subconscious fear of “breaking something” and will help to understand the essence of this or that stage.
Determining the motherboard model
Many find it difficult to determine the model of their motherboard - as with other knowledge of a similar plan, there is one and the same problem: there is no urgent need to memorize or memorize an intricate set of letters and numbers, and this does not help in everyday tasks. Referring to the documentation or looking for a box is also not an option - many tend to lose such things when moving, take them somewhere for storage, or simply forget about them. Also, this problem may arise for those who bought a PC "hand-held", although in a store when selling an assembled system unit, boxes from some devices are also in the habit of not giving boxes from some devices, and buyers are reluctant to take them with them.
There are four ways to understand which model you have "motherboard". Of these, three involve the use of utilities, and one - direct access to the board. The latter will not work if you have a laptop: it is not recommended to disassemble them for a non-professional, and the pros do not always cope - the maintainability of modern solutions is mediocre. The same applies to All-in-One PC and any other solutions not mounted in a standard system unit. Also, do not do this if your PC is under warranty service: all screws will be covered with seals, which will easily show whether the device was opened. It is not necessary to make any manipulations - the very presence of their damage is already a sufficient reason for refusing warranty service, which is clearly spelled out in the conditions of any such company.
If nothing prevents you from opening the system unit, it unscrews two / three / four, or, more simply, all the existing bolts and remove the cover from the side. Our eyes will see a motherboard, on the surface of which a sticker will be waiting for you.

That's all: we remember or rewrite the model, we do all the manipulations with the lid in reverse order.
In the case of programmatic verification, the command line, which is available in any version of the operating system of the Redmond company, can also help. After opening it, you will need to type two commands there, activating each by pressing Enter.
wmic baseboard get Manufacturer wmic baseboard get product
The first will provide information on the component manufacturer, and the second - on the model. If you don't want to deal with the command line and disassembling the system unit, then the AIDA64 (formerly Eevrest) and msinfo32 utilities can be a quick alternative. It is worth downloading their free versions from the official sites - the full functionality will most likely not be useful to you, but there is always a chance to catch a virus. In AIDA64, you just need to go to the "Motherboard" section from the start window, and in msinfo32 - to the System Information tab and read the data opposite the Motherboard item.


For Linux-based systems (including Ubuntu, Linux Mint and the like), you need to activate the command dmidecode.
There, among all the data, you must select the items Manufacturer and Product Name.
Do I need to back up my BIOS?
You need to understand that firmwares for BIOS are created by people, and the array of information for well-coordinated interaction must be clearly calculated, and all points must be clearly planned. And if in theory this is possible, then in practice this does not always happen: there is a high probability that a flashing of this system along with a number of improvements can bring a number of problems with a PC into your life, so it is still worth protecting yourself in case of such an opportunity.
Manufacturers themselves do not provide such an opportunity, allowing only more than one firmware version to be written to the medium and then used. But this does not always happen, since no one expects an unfavorable outcome by undertaking such an operation.
This functionality is provided by a third-party program called the Universal BIOS Backup ToolKit. This product was made by an enthusiastic programmer from China in rather distant 2008 and works perfectly on operating systems of the Windows family with versions from XP to 8.1 inclusive. An important feature of this program is its well-coordinated work: the backups are correct, the probability of damage to the final file is close to zero, and the software works surprisingly efficiently, as for an enthusiast. You only need to start it by clicking on the right mouse button with a call to the sub-item "Run on behalf of the Administrator" - otherwise, errors in the work simply cannot be avoided.

The only pitfall that may come across an unfamiliar with the question: most antivirus programs recognize it as malware, which is not true. Of course, they can infect the source file, but even a utility downloaded from the official site will not pass the test of most programs of this class from the first echelon. The reason for this is the specific driver, thanks to which the software has such a unique functionality. In fact, it does not carry any harm, it is only important to download it from a trusted source. The program interface is English, but very simple. A small window contains only a few buttons, the meaning of which will be clear not only to an experienced user, but even to an inexperienced in this matter. In addition to the exit button and the key that calls the documentation reading, the program window has buttons to start copying. After the completion of the process, which takes from one to two to three minutes, an archive in the .rom format will be available in the program folder (or any other one specified by the user), which is a complete copy of your firmware. The size of the memory, which is indicated on the left, is determined automatically, but it is better to double-check it for your motherboard model - in case of a failure, there will be problems and using an incorrectly made copy will not work due to inevitable errors in the future. The likelihood of its success on the UEFI BIOS is doubtful, but further updates of the program should fix all the shortcomings, and maybe they have already been corrected at the time of reading this article.
General information about firmware via DOS
DOS firmware is one of the safest options for reinstalling software for a given computer node, since all problems associated with the incorrect operation of your operating system are simply excluded. There are slightly different process variations for different models of laptops and motherboards on computers, although most of them have many similar features and the guide to flashing in this way can be reduced to a universal series of actions that need to be taken.
Prepare a media for flashing. This can be a floppy disk or a USB flash drive.
In direct comparison, they are in no way inferior to each other, if we talk about this process, but it is recommended to take out a floppy disk only if the motherboard (or BIOS) does not have support for booting from a USB flash drive. If you nevertheless decide to use a more outdated option, then you should check the floppy disk for integrity by inserting it into the computer, going to "My Computer" and calling the disk check in the properties of the media that appears in the list (in our case, it is a floppy disk). If any errors occur, do not expect a miracle from a faulty floppy disk - there is a high probability of malfunctions in the process of "uploading" files and incorrect operation of the PC up to breakdown and the need to carry it for repairs.
Read the official recommendations given by the manufacturer on the official website. Similar manuals can also be found in the instructions for the motherboard, but the data tend to become outdated and it is quite possible that the same happened in your case.
Also, during the flashing process, you will be prompted to download the files necessary for this, which include at least a utility for formatting the media and a firmware file from the list.
Make a backup copy of the data on the media.
Everything is simple here: if any important data remains on a flash drive or floppy disk (which is unlikely), then it is necessary to save them on the computer's hard disk: during the firmware upgrade, they will not be lost, but the removable disk will need to be formatted.
Formatting the disk.
A special utility that runs on behalf of the Administrator will help here. Perhaps this is not in the recommendations, but the launch of any program of such a plan must be performed in this way, otherwise you can get a large number of "difficult" problems and a stopped firmware process. You can also format it using built-in tools by clicking on the disk icon in My Computer and selecting the item of the same name. All values should be left by default, nothing needs to be changed. Should I do full formatting? It will take a long time, so it’s better to simply leave the “fast” checkbox on - the effect will be about the same.
Copying the firmware file.
This stage can be carried out both with the help of a utility, and it can be done using the usual Explorer, with which we usually perform all operations with files on our computer. An important feature is that there should be no extraneous files on the medium - formatting (point 4) is mandatory, deleting the files is indispensable.
It is worth pressing the restart button (it does not matter, on the case or in the system menu) and when loading the initial screen, press the button to enter the BIOS - Delete. After that, we see a menu where you need to select a boot partition: it will be called Boot. In this tab, you need to change the boot priority from the media and put the first one on which the firmware file is written. After making all the preparations, press the F10 key (save all changes and reboot) and follow the instructions given for your specific motherboard model - here the process may differ significantly.
BIOS update via Windows
The option to update the BIOS firmware through the operating system is provided by almost every motherboard manufacturer: each of them has its own utility that does everything in an almost automatic mode. Nevertheless, it is worth carefully studying all the instructions so as not to be confused at the most inopportune moment.
As described in the previous paragraphs of this article, you need to go to the manufacturer's website and select your motherboard model. In the accompanying tabs, the corresponding utilities will be available for download along with the firmware files - in most cases, the process is identical even for products from different companies. Next, you need to run the utility (with Administrator rights, of course) and select the firmware method (item "From file" or similar in meaning). Next, we look in the file manager for the place where we saved the archive and press the "Run" button - the program does the rest automatically. The advantage of this method is simplicity - even a beginner in mastering a PC can cope with it. Another thing is whether a newbie needs to flash the BIOS, because, as mentioned earlier, the procedure can damage components and negatively affect the operation of the computer. It is worth noting that the already small probability of a system failure or a power outage is superimposed on a considerable chance of a failure in the operating system itself - despite all their stability, these software products are extremely complex: even on slightly different configurations, they can lead themselves in completely different ways, because the number of factors that can affect this is extremely large. It is also necessary to warn users who nevertheless decided on such a move: it is not recommended to launch any programs or leave the browser, torrent client or office document running - any combination can affect the operation of the built-in utility and then contacting the service center cannot be avoided. The problem is in the OS itself, which has a lot of components and thousands of possible bugs, which take years to fix even for companies like Microsoft.
In truth, firmware using utilities is far from the best idea, and if there is such an opportunity, then it is better to use more reliable options: firmware via DOS or via the built-in BIOS toolkit. Such solutions are possibly less simple and economical in time, but give a much more predictable effect, which cannot be said about the option described above. In cases of firmware using other methods, the number of factors that can negatively affect the process is minimal, and when the operating system with all its shortcomings is included in the equation, the probability of failures increases by an order of magnitude.
MSI
Unlike even larger market players, this company provides the ability to flash BIOS using any available method from the ones described above. This is convenient, since the system BIOS menu is too tough for many, and some are worried about safety and are ready to play it safe, not wanting to use a utility launched from under the operating system. There is also a variant of firmware via loading into DOS, which is also safe and relatively simple - here the choice must already be made by the user based on an objective assessment of his capabilities and his willingness to minimize or accept the risks.
Whatever the process and whichever method is used, you need to start by determining the model of your motherboard, which can be done in several ways, described earlier in this article. On the official website of the manufacturer, we are looking for our model and download the necessary files, following the instructions. But since there are already three paths themselves, users will clearly not be satisfied with such a simple explanation and will ask to describe the process in detail.
Live Update
Live Update is a utility produced by the company for flashing the BIOS and some other similar manipulations. It is worth noting that MSI motherboards are installed in laptops, tablets and other devices - here it will not help and you will have to use other methods. This is due to the fact that during the firmware process, unexpected errors may occur, which will become critical for the operability and functioning of the device.
So, download the utility from the official website and install it (with the launch of the installer with Administrator rights). This will solve the problem of unexpected failures that so often occur in work after a conflict of programs and permissions. Next, start the program and go to the appropriate item (tab). It is also necessary to simultaneously download the archive with the firmware, because the automated version, according to reviews, does not always work correctly and it is better to refrain from using it.

Then, following the menu, we will have to face a warning that calls to close all open programs (which was already mentioned here earlier) and wait for the end of all the actions that the program performs. Then, of course, the PC will reboot and with the help of the same program it will be possible to find out about the overall success of the operation.
There is another version of the program's operation, which offers an automated installation of a firmware update via DOS, which was described in earlier sections of the article. It should be noted that it retains all the advantages of this method and allows an easy and safe installation of a software upgrade. Technically, the program only downloads the archive with the firmware, so the further process does not differ from the "manual" installation, but you no longer need to search for the required version of the motherboard and download the archive - the utility is responsible for all this. The negative point is that you may not need the newest version, but the software will download it, and the largest numbers in the version column do not guarantee the best performance, as we have seen many times in many cases.
MFLASH is a utility from MSI that is built into the BIOS and allows you to install updates directly from the toolkit of this system. In order to exploit it, no additional tricks are needed: just an empty (or better - formatted) USB flash drive and a file with BIOS software downloaded to it. Here, the sequence of actions is slightly different: the first of them should be just downloading the file mentioned above for your model. Then it will be necessary to clear space - the presence of other files is undesirable, although some users speak positively about the success of such an installation.
After rebooting, you will need to enter the BIOS with the Delete button and find the tab with the same name as the utility. Next, you will need to specify the path to the file (disk) and click on the button to start the process. The length of the entire procedure after entering the BIOS is only a couple of minutes maximum, and after rebooting you will get a system that is most likely to work correctly - there is no chance that it may be affected by any software failures.

From under DOS
Also a reliable method that does not involve the system at all and works great when updating software. In order to find it, it will be necessary to peep among the files on the official one that is necessary for installation from under this OS - in the name there at the end there will be a corresponding mark, as in the screenshot. Next, you need to get a floppy disk, check it for errors using the built-in Windows utility and format it there. If there are no errors when checking the disk, then it will be possible to write a file to it - it will become the installation file.
Next, reboot and enter the BIOS with the Delete button. After this has happened, we are looking for the Boot Device Priority item and put our floppy drive in the first place. Then press F10, agree to save all changes and wait for the reboot.

After loading the operating system, we will see a black background with fonts in bright colors (or white) - it means we are logged in. We will be prompted to press Y to continue and N to leave this mode. We press the first button, wait for a minute and a half and see an inscription about the successful completion of the firmware upload. We remove the floppy disk and restart the computer, along the way entering the BIOS and changing the boot priority again to the hard disk, although if the floppy disk is removed and there is no boot disk in the drive, it will do this anyway.
Gigabyte
Gigabyte is the third largest motherboard manufacturer in the world, with main facilities and headquarters in China. The company did not previously have such technologies and was just a contractor for large "sharks" of the market such as Asus or Intel, but after "peeping" from them some developments and opening soybean research departments, it quickly turned from an apprentice into full-fledged competitors.
Gigabyte's specialists in BIOS software did not reinvent the wheel: all methods of reinstalling software for this system are as similar as possible and are clearly borrowed from other market players. It is not known for certain whether there are patent wars between corporations, but one thing is for sure: the user wins from such solutions, because all the actions and methods of changing the firmware that Asus and MSI work with also work on the motherboards of the Chinese company - only the appearance differs (especially formally) and the names of the utilities. The company did not come up with something fundamentally new, which had a positive effect on the convenience of such operations.
A positive point is that the company in every possible way contributes to the ease of searching for its documentation, which is not hidden in the bowels of the official website, but is easily achievable within the search results of any system on the first page in several copies.
The company, or rather, its experts strongly advise against carrying out such a procedure, unless you have identified any malfunctions and failures in the operation of the equipment: processor, RAM and other components. In many cases, according to research by the company itself, performance does not improve and degrades, so it is worth carefully considering the advisability of flashing the BIOS.
Also in the manuals, much attention is paid to the exact definition of the motherboard model, taking into account the revision. Since the Gigabyte lineup contains models that are designated the same, but one of them is a re-release of the second, the firmware (and all other manipulations) may differ, the use of the wrong archive can be reflected in the most disastrous way.
It is also worth noting that in the event of a breakdown or any other malfunction that may occur in the event of a flashing of the warranty, the device is not subject to, because this action is fully qualified as a repair. This is also worth considering, and it is good that the manufacturer is not silent about this.
Q-Flash is the most reliable way of flashing BIOS: this utility is built into the system itself and performs its functions perfectly, with minimal predisposition to incorrect firmware. Its operation does not depend on the operation of the operating system, which is an undoubted advantage. The only problem is that not all solutions support this technology - in other situations, a much simpler solution would be firmware via DOS.

Before using the Q-Flash utility, you need to download the most current BIOS version that matches your motherboard model from the GIGABYTE official website. The file with the BIOS microcode must be written to a medium (floppy disk, flash drive or hard disk; file system FAT32 / 16/12).
Since the BIOS microcode update procedure carries a potential risk, it is not recommended to update the BIOS unless the current BIOS version is satisfactory. Updating the BIOS should be done very carefully. Incorrect BIOS update may result in system malfunction.
This solution allows you to update the firmware of the I / O system from under the good old operating system such as DOS. It should be noted that the flashing operation must be performed on a system operating normally. Overclocking, low memory timings, non-standard system bus frequency can lead to the fact that our event will end with a trip to the service center (or a call to familiar gurus). The easiest way is to load the default settings into BIOS SETUP (Load Fail-Safe Defaults main menu item or similar).

The flashing operation must be performed only from under DOS. To boot from a floppy disk, there are only two system files on it: io.sys and command.com. In any case, neither autoexec.bat nor config.sys should be loaded. In addition, the floppy disk must contain files with the flasher and the firmware itself.
Run the flasher with the "/?" and you will receive detailed instructions on how to work with it.
Please note that the updated firmware does not always meet the user's expectations. Be sure to save the file with the old BIOS version on a floppy disk (!) In order to be able to reverse your actions in the future. For AWARD BIOS, calling the flasher can be as follows: “awdflash.exe newflash.bin / py / sy”. Where “newflash.bin” is the real name of the file with the firmware, “py” and “sy” are the flags for reprogramming and saving the old BIOS version, respectively. And the last thing: under no circumstances restart or turn off the computer until the flasher has finished working. This will lead to imminent BIOS corruption.
Live Update
Live Update is perhaps the simplest solution to problems with the I / O system, because it looks for the necessary microcodes and does almost all the manipulations instead of the user - you do not need to be any specialist in this area to use it. To get started, you need to go to the official website and download the Live Update 5 utility, which will scan your computer and give you a list of necessary updates, with the ability to download them. Click "Click here" and click "Open".
The archive will open, run the LiveUpdate.exe installation file in it and install the Live Update 5 utility in a few steps. After the installation is complete, launch it and click on the "Scan" button, wait a few seconds while the utility searches for updates. The program will display a list of results. We are interested in an update called "MB BIOS". If such an update is listed (usually at the very top), then there is a BIOS update for our motherboard. Download it to your computer by clicking on the "Download" button (arrow). Better to click "Browse", and choose a location to save the update file yourself. For example, I saved it to the desktop. That's it, we now have the BIOS update file, now we can proceed to the next stage. Run the saved BIOS update file and follow the instructions.
There are two options here: the first is probably to write the firmware image to a USB flash drive, and update the BIOS from the flash drive (or for firmware, if it is impossible to update from under Windows). But since I did not have a free flash drive, I chose the second option, which, judging by the title, means BIOS firmware from under Windows. Here we need to close running programs and click "Next".
The further process of updating the BIOS is that we simply press any key on the keyboard, and the computer must reboot. Then everything is over - the device has received a new firmware.
ASUS BIOS firmware
ASUS is one of the titans of the computer components industry, which is proving to be market leaders both quantitatively and qualitatively. An important feature of their products is ease of maintenance: for each class of goods there is a utility that searches for drivers or any other useful work - in the case of this company, the implementation of these solutions is at its best. The same happened with updating the BIOS: both options are very convenient and easily mastered by unskilled and inexperienced users.
USB BIOS Flashback is the easiest way to update BIOS on ASUS motherboards. To update, now all that is needed is a USB drive with a BIOS file recorded on it and a power supply unit. No processor, RAM or other components are needed anymore.
The list of system requirements for this utility is rather prosaic:
- power unit;
- USB drive FAT16, FAT32 or NTFS (for Intel X79 only FAT16 and FAT32);
- ASUS motherboard based on Intel X79, Z77, H77, Q77, B75 chipsets (the list of ASUS motherboards that support USB BIOS Flashback technology is presented in the table).
First, you need to download and unpack the BIOS ROM file from the ASUS official website. It is important to understand that receiving files from somewhere else is fraught with irreversible consequences and unexpected equipment operation. Next, you should rename the BIOS file as written in the table, and then save it to a USB drive in the root directory:
| Model | File name |
| P9X79 Deluxe | P9X79D.ROM |
| P9X79 Pro | P9X79PRO.ROM |
| P9X79 | P9X79.ROM |
| Sabertooth X79 | SABERX79.ROM |
| Rampage IV Extreme | R4E.ROM |
| Rampage IV Formula | R4F.ROM |
| Rampage IV Gene | R4G.ROM |
| Р8Z77-V Deluxe | Z77VD.CAP |
| P8Z77-V Pro | Z77VP.CAP |
| P8Z77-V | Z77VB.CAP |
| P8Z77-V LE | P8Z77VLE.CAP |
| P8Z77-V LX | P8Z77VLX.CAP |
| P8Z77-V LK | P8Z77VLK.CAP |
| P8Z77-M Pro | P8Z77MP.CAP |
| P8Z77-M | P8Z77M.CAP |
| Sabertooth Z77 | Z77ST.CAP |
| Maximus v gene | M5G.CAP |
| P8H77-V | P8H77V.CAP |
| P8H77-V LE | P8H77VLE.CAP |
| Р8H77-M Pro | P8H77MP.CAP |
| P8H77-M | P8H77M.CAP |
| P8H77-M LE | P8H77MLE.CAP |
| P8B75-V | P8B75V.CAP |
| P8B75-M | P8B75.CAP |
| P8B75-M LE | P8B75LE.CAP |
| P8Q77-M | P8Q77.CAP |
| P8H77-I | P8H77I.CAP |
Then you should connect the USB drive to the USB BIOS Flashback / ROG Connect connector (for boards based on Intel X79 this is a white USB 2.0 connector, for boards on other chipsets this is a USB 2.0 connector marked with color and the inscription USB BIOS Flasback / ROG Connect on the panel Q-Shield) and hold for three to four seconds until the light indication starts. Next, we are waiting for the completion of the light indication of the USB BIOS Flashback / ROG Connect button, which means that the update was successful.

It is important not to remove the USB drive, power off the motherboard, or press the CLR_CMOS reset button while updating the BIOS. It is also worth remembering that if the USB BIOS Flashback / ROG Connect button blinks for five seconds, then USB BIOS Flashback is not working correctly. This may be caused by improper installation of the device, an error in the file name, or an incompatible file format - you should check it yourself after a reboot. It is worth noting the company's rather loyal policy regarding problems after updating the firmware: in case of any problems with booting after updating the BIOS, you can contact the local representative of the ASUS service, which, according to the statements of the authors of the documentation, undertakes to help.
AFUDOS utility
This solution is a bit outdated - EZ Flash is the most popular utility on motherboards released in the 2000s and 2010s, although the old solution is also applicable for many devices. To start the firmware in a similar way, open the bootable USB flash drive, write the afudos program to it (the afudos.exe file downloaded from the site) and the firmware itself (a file with a type name p5c800b.rom). Then we reboot and when the first picture appears on the monitor, press F2 for laptops or Del for desktop PCs, go to the Boot tab and put the USB flash drive in the first place, usually for this in the 1st Boot Device item you need to set Removable Device, then press F10 and confirm that we want to save the changes in the settings. After that, the computer will boot from the flash drive, and will display a prompt to work A: \> on a black screen. To start the firmware process, write afudos /ip4c800b.rom and press the Enter key. It is worth noting that you do not need to turn off the power or reboot the system during the BIOS update. This can cause serious damage to your system. After completing the BIOS update, the utility will return to DOS, you should remove the floppy disk and reboot the system to enter the BIOS menu.

Intel
This method is one of the simplest, as it uses a self-extracting archive and does not require any special skills from the user. After selecting the section dedicated to the motherboard, you need to download the firmware, in our case it is Express BIOS Update and run it with a double click. Then click "Next" in the invitation window, and then - "Yes" to accept the license rules. After - click "Finish". Windows will reboot to start updating the BIOS. During the update process, do not turn off the computer power for 3 minutes. During the reboot process, you will see the BIOS update process. When the BIOS is updated, the computer will boot into Windows. When Windows restarts, a window will appear indicating that the BIOS was updated successfully.

The essence of this method is to create bootable (disks, flash drives, floppy disks) containing the BIOS update. In our case, download this file LF94510J.86A.0278.BI.ZIP
For work, we need firmware files (write down its name on a piece of paper, it will come in handy later) with the XXX.BIO extension and the iFlash.EXE firmware utility. These files are in the archive with the downloaded firmware. Use the iFlash utility that comes with the firmware in the archive. Also useful is the HP USB Disk Storage FormatTool 2.2.3 utility (other versions are possible), but this one at the time of this writing is one of the most stable. It goes without saying that you cannot do without MS-DOS files to create a bootable DOS disk. After downloading, all files are unzipped.
Run the utility as administrator HP USB Disk Storage FormatTool 2.2.3. We set the checkboxes as shown in the picture. The path to the folder of the MS-DOS boot device is written in the place where the MS-DOS files were downloaded. (I have, for example, drive C, the Downloads \ win98boot folder. And the Start button. When asked about deleting files, click "Yes".

Upon completion of the process, copy 2 files from the archive with the firmware to the USB flash drive (an example of how they look: IFLASH2.EXE and LF0278P.BIO). And without removing the USB flash drive from the USB port, we restart the computer. We go into the BIOS (F2 button when booting) and set the priority for booting from a USB drive (on the Boot tab, enable booting from USB (Enable USB Boot) and exit the BIOS while saving the settings - F10.
DOS will boot. At the command line, enter IFLASH / PF XXX.BIO (or IFLASH2 / PF XXX.BIO) to start the BIOS update process. Then follow all directions. In our example, it will look like this: IFLASH2 / PF LF0278P.BIO
Creating a bootable floppy is an effective method if the utility and firmware are small enough to fit on a floppy, since the floppy is 1.44Mb in size.
For our example, there is no way to visually show the process of creating a bootable disk. So I'll take another firmware file from another motherboard as an example. Insert the floppy disk into the floppy drive and double-click the downloaded firmware file XXX.EXE. Press "y" to extract the required files. The files will be extracted to a temporary directory (temp folder; path C: \ temp). You can also extract files with the usual WinRAR archiver. Double-click the RUN.BAT file and follow the instructions to create a bootable floppy disk.
After creation, restart the computer, in the BIOS set the boot from the Floppy disk and exit with saving the parameters - F10. After booting from a floppy disk, a welcome window will appear, press any key. You will see the BIOS update status. When the process is complete, remove the floppy disk from the floppy drive and press Enter to restart the computer.
ASRock Firmware
For motherboards from a Chinese manufacturer, the sequence of actions will also not be very different when flashing: here you also need to format the media and go to the official website for files. Further, the list of actions is also standard and is no different from updating from under DOS from other manufacturers ...
Please download the BIOS update file (WinZip file with .zip extension) from ASRock website, unpack it and save ASRFLASH.EXE utility and BIOS file to floppy disk. Next, we boot the system from a floppy disk. At the "A: \" prompt, type ASRFLASH, press the spacebar once and enter the BIOS file name, then press Enter. For example: A: \ ASRFLASH K7S41GX2.00 "Enter". Then you will see the message "Please wait for BIOS loading ROM".
After 30 seconds, you will see the message "Flash ROM Update Completed - Pass", which means that the BIOS update is complete. Remove the floppy disk after BIOS update. Reboot the system and press F2 during boot to enter BIOS setup.
From the Exit menu, select "Load Default Settings" and press "Enter" to continue. Select "Exit Saving Changes" and press "Enter" to exit the BIOS setup utility.
Actions after flashing
It is not necessary to undertake any special "rituals" after the flashing, if it is not provided for by the instructions: it is enough to remove the media that was involved after the flashing and test the operation of the PC with the new software. If you notice any glitches, it makes sense to roll back to the previous version or find another, so that both the support for new components and the stability of the machine do not suffer.





Prolongation of registration of participants in the "Living Classics" competition!
Who deleted me from friends on VKontakte All friends disappeared from the contact
Which operator was the best in Russia
Double cassette tape recorder
"VK" can be closed for a long time