Sometimes the installed application fails to start. And Windows 7 displays a message with an error code or an incomprehensible inscription. The easiest option for further action, taken by many, is to reinstall the program. Although this solution does not always give a positive result. Here are the most common application launch problems accompanied by a message with an error code or description. And ways to solve them.
Application and operating system compatibility error
Such an error occurs when the version of the application being launched is incompatible with Windows 7. Many creators of software products (especially free software) do not have time to develop the latest versions of their programs. Or the user has installed an outdated (outdated) version of the application for Windows 7. Then there may be problems when trying to run it. The system displays a message that an error occurred while starting the application. Or even if the application has started, it will not work correctly. This problem can be solved by native means of the OS. To do this, do the following:

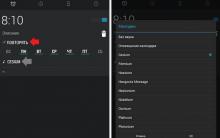
- Click the mouse on the shortcut of the desired application or file with the "exe" extension.
- By pressing the key on the right, we call up its context menu.
- Select "Fix Compatibility Issues" from the list.
- In the Program Compatibility window that appears, select Program Diagnostics.
- In the next dialog box, put a checkmark next to the item with a description of the problem “The program worked in previous versions of the OS” and click “Next”.
- Then we select the OS version in which the application functioned without problems.
- Click "Next".
A window appears with a description of the parameters with which the launch will be carried out. Clicking "Next" starts the program. If these launch options in Windows 7 did not lead to the correct operation of the application:

- In the Program Compatibility dialog box, click on No, try different settings.
- We set new parameters and try to run the program again.
Memory read error
This application startup error can be caused by several reasons. But most of all in Windows 7, it is related to the operation of the DEP service.
DEP is a data execution prevention service. Its main function is to stop the spread of viruses in the computer by blocking access to the system sections of RAM. The service does not interfere with the malware installation process in any way. It only blocks access to certain sectors of the system's memory.
If a program that does not have access rights to one of these partitions tries to enter memory, then DEP immediately stops its work. The result of closing this application is a "Program Error" message. To configure this service, do the following:

- We enter the "Control Panel" through the "Start".
- Select the "System" tab.
- In the list on the left, click on "Advanced system settings".
This procedure in Windows 7 only allows you to configure exceptions for the DEP service by including it in a special list of applications. Programs listed in the list will be allowed access to system memory partitions. You should not include those programs here if you are not sure about their origin and safety.

- In the "Advanced" tab, select the "Performance" item.
- Click on its Settings.
- In the "Performance Options" window, go to the "Data Execution Prevention" part.
- Here we select the item "Turn on DEP for programs and services other than those I select."
- Use the "Add" button to edit the exclusion list.
- Don't forget to click Apply.
Error 0xc0000022
Such an application launch error in Windows 7 occurs due to the lack of any library required for the program to work. Library files have the extension "dll". The reason for the lack of libraries may be the activity of viruses.
Error code 0 x c0000022 also occurs when a user tries to run an incorrectly "cracked" program after installing it. During startup, when the application instance is being initialized, a missing library is accessed. Not finding it, the system displays a message with this error code.
Most often, the appearance of such a message is caused by a problem in the interaction of the video card with the system part due to the lack of the necessary libraries in the program code of the drivers. Possible solutions:

- Update video card drivers.
- Installing the latest version of DirectX.
- Installing all possible updates for Windows 7.
If this did not help, and the attempt to start the application still failed, then you can roll back the system. To do this, select the recovery point (date) during the creation of which the program was launched without problems.
You turn on the computer, a text boot screen appears with numbers and letters flashing quickly. Usually, the computer works fine and you don't pay attention to them. But this is an important part of the computer's operation during which the microprograms built into the BIOS work. But then something incomprehensible happened and everything stopped, an error code is displayed on the screen, and sometimes nothing is displayed at all - the cursor blinks and everything froze in an incomprehensible dream.
How it worksAfter turning on the computer, there is no operating system in its RAM. And without an operating system, the computer's hardware can't do complex things like loading a program into memory. Thus a paradox arises that seems unresolvable: in order to load an operating system into memory, we must already have an operating system in memory. The solution to this paradox is the use of several microprograms placed in one or more microcircuits, the BIOS (Basic Input / Output System). P download process begins with the automatic execution by the processor of instructions located in read-only (or writable) memory (EEPROM or Flash ROM), starting at a given address. This firmware does not have all the functionality of the operating system, but it (functionality) is enough to perform sequential loading of other programs that are executed one after the other until the last one loads the operating system. The sequence of the main blocks of BIOS functions in PC-compatible computers: 1. - POST - power-on self-test of the processor, memory, system logic chipset, video adapter, disk controller, keyboard, mouse and other controllers and devices; 2. - Setup BIOS (BIOS setup program) - configuring system settings. It can be launched during the POST procedure by pressing a certain key combination. If it was not called by the user, the parameters set and saved in permanent memory during the last configuration of the Setup BIOS are loaded. 3. - Operating system loader - a subroutine that searches for a valid main boot sector on a disk device. 4. - BIOS - a set of drivers designed to interact with the operating system and hardware when the system boots. During the BIOS boot process, in addition to the above, connection, disconnection, setting the operation mode of the system board device controllers in accordance with the settings recorded in the permanent memory. Why is this needed? This is needed for:
During its execution, the presence of boot devices is checked, which must be initialized before the operating system is loaded. These include:
The BIOS then polls the devices listed in the pre-created list until it finds a bootable device. If no such device is found, an error message will be displayed and the download process will be stopped. If the BIOS detects a boot device, it reads the bootloader from it and transfers control to it. In the case of a hard drive, the boot loader is called the Master Boot Record (MBR) and is often independent of the operating system. It usually looks for an active hard disk partition, loads the partition's boot sector, and transfers control to it. This boot sector is usually operating system specific. It must load the operating system kernel into memory and transfer control to it. If the active partition does not exist, or the boot sector of the active partition is invalid, the MBR can load the backup bootloader and transfer control to it. The backup bootloader must select a partition (often with the help of the user), load its boot sector, and transfer control to it. |
Boot sequence for a standard IBM-compatible personal computer
After turning on a personal computer, its processor does not start working yet.
The first device that starts after pressing the power button on the computer is the power supply. If all supply voltages are available and correct, a special Power Good signal will be sent to the motherboard, indicating a successful test of the power supply and allowing the motherboard components to start.
After that, the chipset generates a CPU reset signal, according to which the CPU registers are cleared, and it starts up.
The first command to be executed is located at FFFF0h and belongs to the BIOS address space. This command simply transfers control to the BIOS initialization program and executes the next command (the BIOS firmware).
The BIOS initialization program, using the POST program, checks that all the computer devices necessary for the BIOS to work and the subsequent loading of the main operating system are working correctly and initializes them.
So its job is to sequentially read and execute commands from memory.
The system memory is configured so that the first instruction that the processor reads after a reset will be in the BIOS chip.
By successively selecting commands from the BIOS, the processor will begin to perform a self-test, or POST.
POST procedure
The POST self-test procedure consists of several steps.
- Initial initialization of the main system components;
- Detection of RAM, copying BIOS code to RAM and checking BIOS checksums;
- Initial chipset setup;
- Search and initialization of the video adapter. Modern video adapters have their own BIOS, which the system BIOS tries to detect in a dedicated address segment. During the initialization of the video adapter, the first image generated by the BIOS of the video adapter appears on the screen;
- Check CMOS checksum and battery condition. If the CMOS checksum is wrong, the default values will be loaded;
- CPU and RAM testing. Test results are usually displayed on the screen;
- Connecting a keyboard, testing input / output ports and other devices.
- Initialization of disk drives. Information about discovered devices is usually displayed on the screen;
- Distribution of resources between devices and output of a table with discovered devices and resources assigned to them;
- Search and initialization of devices with their own BIOS;
- Call BIOS software interrupt INT 19h, which looks for the boot sector on the devices specified in the boot list.
Depending on the specific BIOS version, the order of the POST procedure may vary slightly, but the above basic steps are performed when any computer boots.
What are POST codes?
After turning on the power of the computer, if the power supply and the main components of the motherboard (clock generator, components responsible for the operation of the system bus and memory bus) are working, the processor starts executing the BIOS code.
To be precise, in many modern chipsets, before sending commands to the processor, the system controller pre-configures the "smart" system bus. But this does not change the essence of the matter.
The main task of the BIOS at this stage is to check the health and initialize the main hardware components of the computer. First, the internal registers of the chipset and processor are configured, and the integrity of the BIOS code is checked. Then the type and size of RAM is determined, the video card is searched and initialized (integrated into the chipset or external). Next, the I / O ports, the drive controller, the IDE / SATA controller and the drives connected to it are configured. And, finally, the search and initialization of additional controllers integrated on the motherboard and installed expansion cards is carried out. In total, about a hundred intermediate steps are obtained, after which control is transferred to the BOOTStrap loader, which is responsible for starting the operating system.
Each of the POST test steps has its own unique number, called the POST code. Before starting the execution of the next procedure, its POST code is written to a special port called the Manufacturing Test Port. Upon successful initialization of the device, the POST code of the following procedure is written to the Manufacturing Test Port, and so on, until all tests are passed. If the device configuration fails, further POST tests are terminated, and the POST code of the procedure that caused the failure remains in the Manufacturing Test Port. After reading it, you can uniquely identify the problem device.
Keep in mind that after rebooting the computer using the operating system (“soft” or “hot” reboot) or when exiting the energy-saving mode, not all steps for testing and configuring hardware components are usually performed, but only the necessary minimum - it’s faster this way. When troubleshooting, you must always perform a "hard" ("cold") reboot - by pressing the RESET key or turning off the computer's power. This is the only way to ensure that all initialization steps are completed in full.
Award BIOS 6.0: Full Boot Option
This table can be used not only as a list of POST codes, but also as a sequence of actions that are performed when the computer is turned on. It contains the POST codes that are displayed during the full POST procedure.
| POST code | Description of the procedure |
| CF | Processor type is determined and CMOS read/write is tested |
| C0 | The chipset and L1-, L2-cache are pre-initialized, the interrupt controller, DMA, timer are programmed |
| C1 | The type and amount of RAM is detected |
| C3 | BIOS code is decompressed into a temporary area of RAM |
| 0C | Checking BIOS checksums |
| C5 | The BIOS code is copied to shadow memory and control is transferred to the Boot Block module |
| 01 | The XGROUP module is unpacked at physical address 1000:0000h |
| 02 | Processor initialization. CR and MSR registers are set |
| 03 | I/O resources are defined (Super I/O) |
| 05 | Clears the screen and CMOS status flag |
| 06 | Coprocessor being checked |
| 07 | Keyboard controller defined and tested |
| 08 | The keyboard interface is defined |
| 09 | Initializing the Serial ATA Controller |
| 0A | Detects keyboard and mouse connected to PS/2 ports |
| 0B | Installing AC97 audio controller resources |
| OE | Memory segment F000h is being tested |
| 10 | The type of flash memory is determined |
| 12 | CMOS tested |
| 14 | Set values for chipset registers |
| 16 | The clock generator is initially initialized |
| 18 | The processor type, its parameters and L1 and L2 cache sizes are determined |
| 1B | Interrupt vector table initialized |
| 1C | CMOS checksums and battery voltage are checked |
| 1D | The Power Management system is defined |
| 1F | Keyboard matrix is loading (for laptops) |
| 21 | Hardware Power Management is initializing (for laptops) |
| 23 | Tested math coprocessor, floppy drive, chipset initialization |
| 24 | Processor microcode is updated. A resource allocation map for Plug and Play devices is created |
| 25 | PCI initialization: enumerate devices, search for VGA adapter, write VGA BIOS at C000:0 |
| 26 | The clock frequency is set by CMOS Setup. Disables synchronization of unused DIMM and PCI slots. The monitoring system is being initialized (H/W Monitor) |
| 27 | Interrupt INT 09h is enabled. Keyboard controller initialized again |
| 29 | MTRR registers are programmed, APIC is initialized. The IDE controller is being programmed. Processor frequency is measured. The video system BIOS extension is called |
| 2B | Finding the video adapter BIOS |
| 2D | The Award splash screen, information about the type of processor and its speed is displayed |
| 33 | The keyboard is reset |
| 35 | First DMA channel being tested |
| 37 | Second DMA channel being tested |
| 39 | DMA page registers are tested |
| 3C | The 8254 controller is configured (timer) |
| 3E | Checking the 8259 Interrupt Controller |
| 43 | Interrupt controller checked |
| 47 | ISA/EISA tires tested |
| 49 | The amount of RAM is calculated. Adjust registers for AMD K5 processor |
| 4E | The MTRR registers for the Sirix processors are being programmed. L2 cache and APIC are initialized |
| 50 | USB bus defined |
| 52 | RAM is tested with results displayed. Expanded memory is cleared |
| 53 | If the CMOS is cleared, the login password is reset |
| 55 | The number of processors is displayed (for multiprocessor platforms) |
| 57 | The EPA logo is displayed. Initialization of ISA PnP Devices |
| 59 | The system of protection against viruses is determined |
| 5B | Displaying a prompt to run a BIOS update from a floppy disk |
| 5D | Super I/O controller and integrated audio controller start up |
| 60 | Entering CMOS Setup if the Delete key was pressed |
| 65 | PS/2 mouse initialized |
| 69 | Enable L2 cache |
| 6B | Chipset registers are configured according to BIOS Setup |
| 6D | Assign resources for ISA PnP devices and COM ports for integrated devices |
| 6F | Initializing and configuring the floppy disk controller |
| 75 | IDE devices are detected and installed: hard drives, CD/DVD, LS-120, ZIP, etc. |
| 76 | Displays information about detected IDE devices |
| 77 | Initialize serial and parallel ports |
| 7A | The math coprocessor is reset and ready to work |
| 7C | Defines protection against unauthorized writing to hard drives |
| 7F | If there are errors, a message is displayed and the Delete and F1 keys are expected to be pressed. |
| 82 | Memory is allocated for power management and changes are made to the ESCD table. The splash screen with the EPA logo is removed. Requires a password if needed |
| 83 | All data is stored from the temporary stack in CMOS |
| 84 | Displaying the message Initializing Plug and Play Cards |
| 85 | USB initialization complete |
| 87 | SYSID tables are created in the DMI area |
| 89 | ACPI tables are installed. Assign interrupts to PCI devices |
| 8B | Called by the BIOS of additional ISA or PCI controllers, except for the video adapter |
| 8D | RAM parity parameters are set by CMOS Setup. APM is initialized |
| 8F | IRQ 12 is allowed for hot plugging a PS/2 mouse |
| 94 | Completion of chipset initialization. Displays the resource allocation table. Enable L2 cache. Setting the daylight saving time mode |
| 95 | Sets keyboard auto-repeat frequency and Num Lock state |
| 96 | For multiprocessor systems, registers are configured (for Cyrix processors). The ESCD table is created. The DOS Time timer is set according to the RTC CMOS clock. Partitions of boot devices are saved for use by the built-in antivirus. The speaker announces the end of POST. MSIRQ FF table is created BIOS interrupt INT 19h is executed. Searching for the bootloader in the first sector of the boot device |
Failure or failure of any step in the test sequence leads to a stop of testing and the issuance of a POST code corresponding to this step of failure.
POST codes from other manufacturers can be found on your motherboard or DIOS manufacturer 's websites or on the Internet .
Reading POST Codes
In workshops or at the repair specialists, the control of the BIOS firmware is carried out using a special expansion card. It is inserted into a free slot (most modern models are designed for the PCI bus) and, as it loads, it displays on its indicator the code of the procedure currently being performed.
An example would be a PCI Post Card BM9222.
However, the POST card is not a widely used tool. Rather, it is a professional computer repair tool. Realizing this fact, motherboard manufacturers began to equip models designed for enthusiasts experimenting with settings and overclocking a computer with built-in POST code indicators.
An example would be the ECS H67H2-M motherboard, or models X58 Extreme3, P55 Deluxe3 and 890GX Extreme3.
There is also a cheaper solution - during the initial initialization of components, POST codes can be displayed on the screen along with other service information. True, this solution has a significant drawback: if the problem is related to the video card, you most likely will not see anything.
The last opportunity to learn about the failure manifested during testing Beep error messages.
Sound signals and error messages
Despite the fact that POST codes are the most powerful tool for identifying hardware problems when starting a computer, the BIOS provides other diagnostic tools. If you do not have a POST card at your disposal, and the motherboard cannot display POST codes, you can focus on beeps and error messages.
But for this it is necessary that the PC case has a system speaker and it is connected to the motherboard.
Sound signals are especially valuable at the initial stage, when the video card has not yet been initialized and, as a result, is not able to display anything on the screen. A unique combination of long and short signals will indicate the problematic component.
In later stages, it is easier to navigate by the error message displayed by the BIOS in the event of a hardware problem. In some BIOS versions, this message is accompanied by a special beep, in some it replaces it. But in any case, the information is usually enough to identify the failing component.
It should be noted that sound signals and error messages are actually a more visual option for displaying certain POST codes, and by no means an additional diagnostic tool. If you have a POST card at your disposal, or the motherboard is capable of displaying POST codes, you need to focus on the codes - they give a much more accurate and detailed picture. Compare at least the number of POST codes (about a hundred) and the number of different error messages or beeps (a few dozen).
| Beep sequence | Error Description |
|---|---|
| 1 short | Successful POST |
| 2 short | Minor bugs found. A prompt appears on the monitor screen to enter the CMOS Setup Utility program and correct the situation. Check the reliability of the fastening of the cables in the connectors of the hard drive and the motherboard. |
| 3 long | Keyboard controller error |
| 1 short, 1 long | Random Access Memory (RAM) Error |
| 1 long, 2 short | Video card error |
| 1 long, 3 short | Keyboard initialization error or Video card error |
| 1 long, 9 short | Error while reading from ROM |
| Repetitive short | Problems with the power supply |
| recurring long | RAM problems |
| Repetitive high-low frequency | CPU issues |
| Continuous | Problems with the power supply |
Setup procedure
Entering BIOS Setup
You can enter BIOS Setup only when the computer is turned on and the initial POST is successfully completed (one short beep is heard from the system speaker).
To do this, you must press a specific key or key combination.
Usually, the screen saver during testing displays an inscription like “Press DEL to enter Setup” - this means that you must press the DEL key to enter BIOS Setup. You can find out which key is assigned to enter the BIOS from the instructions for the motherboard. If there is no instruction, and the screen saver does not display tips, you can try the most famous combinations:
Delete
Esc
Ctrl + Shift + S or Ctrl + Alt + S
Ctrl + Alt + Esc
Ctrl+Alt+Delete
Safe work with BIOS Setup
Working with BIOS Setup is associated with a certain risk, since if the parameter is changed incorrectly or carelessly, the system may function unstable or not function at all. There are a few simple tips to help minimize the potential risk:
- It is best to experiment with BIOS Setup settings on a new computer that has not been filled with information;
- Try not to experiment with the BIOS at all on computers that process or store important or large information. Before configuring the system using the BIOS, take care to back up important data. The main thing in such computers is stability. A hung overclocked computer after several hours of video processing is a waste of time, energy and the result of work. An overclocked one will cope with this task much more efficiently and save your nerves;
- Before changing important parameters, always fix the set and changed value. This will allow you to return it to a working state in case of unstable operation of the system;
- Do not change the values of parameters that you do not know. Specify their meaning either in the instructions for the motherboard, or on the Internet on the resource of the board developer;
- Do not edit several important unrelated parameters at the same time. When the system is unstable, it is much more difficult to determine which parameter caused the instability;
- Do not overclock your computer without proper study of the operation of the overclocked system and preparation;
- Do not use the Hard Disk Utility section, which is designed for low-level formatting of obsolete hard drives and is found in older BIOS versions. can disable a modern hard drive;
- If, after setting the parameters and exiting the BIOS, the computer stops starting at all, there are several ways to return the system to a working state:
- If after rebooting the computer it is possible to enter the BIOS Setup, you need to set the previous values of the edited parameters. Some BIOS versions themselves roll back changes from the last session.
- If the changes made are unknown, it is best to use the default settings using the Load Fail-Safe Defaults command. After that, you will have to configure the system for optimal operation.
- If the computer does not start at all due to incorrect BIOS settings, then in this case it is necessary to reset the contents of CMOS. In this case, all values including date/time will be changed. To reset incorrect settings, simply move the Flash Recovery (IBM) jumper or the Clearing CMOS jumper to the "clear CMOS" position. In the latter case, you just need to close the contacts of the corresponding jumper with a jumper for a few minutes.
- In case of unsuccessful results of the Setup BIOS setup, it is necessary, after resetting the unsuccessful configuration using the jumper in the Setup BIOS procedure, to duplicate the return loading of BIOS values en.Wikipedia.org<< на главную>>
Manually editing the Windows registry to remove invalid Error 5 keys is not recommended unless you are PC service professional. Mistakes made while editing the registry can render your PC unusable and cause irreparable damage to your operating system. In fact, even a single comma in the wrong place can prevent your computer from booting up!
Because of this risk, we highly recommend using a trusted registry cleaner such as WinThruster [Download] (Developed by Microsoft Gold Certified Partner) to scan and repair any Error 5 related issues. By using the [Download] Registry Cleaner, you can automate the process of looking for broken registry entries, missing file references (such as those causing the %%error_name%% error), and broken links within the registry. A backup copy is automatically created before each scan, allowing you to undo any changes with a single click and protecting you from possible damage to your computer. The best part is that fixing [Download] registry errors can drastically improve system speed and performance.
A warning: Unless you are an advanced PC user, we do NOT recommend editing the Windows Registry manually. Incorrect use of the Registry Editor can lead to serious problems and require you to reinstall Windows. We do not guarantee that problems resulting from misuse of Registry Editor can be corrected. You use the Registry Editor at your own risk.
To manually repair your Windows registry, first you need to create a backup by exporting part of the registry related to Error 5 (eg. Windows Operating System):
- Click on the button Begin.
- Enter " command" in search bar... DO NOT PRESS YET ENTER!
- Holding keys CTRL-Shift on the keyboard, press ENTER.
- An access dialog will be displayed.
- Click Yes.
- The black box opens with a blinking cursor.
- Enter " regedit" and press ENTER.
- In the Registry Editor, select the Error 5-related key (eg. Windows Operating System) you want to back up.
- On the menu File select Export.
- Listed Save to select the folder where you want to save the Windows Operating System key backup.
- In field File name enter a name for the backup file, such as "Windows Operating System Backup".
- Make sure the field Export range value selected Selected branch.
- Click Save.
- The file will be saved with .reg extension.
- You now have a backup of your Windows Operating System-related registry entry.
The next steps for manually editing the registry will not be covered in this article, as they are likely to damage your system. If you would like more information on editing the registry manually, please see the links below.
(Created to accompany clients of Praktika LLC)
Important! Before making any changes in the 1C database, make a backup copy. If 1C is launched in the configurator mode, then through the menu Administration -> Save data. If you already have older copies, don't overwrite them, make a separate archive. If 1C does not start in configurator mode, copy the entire database directory to another location. If you have another storage medium (a second hard drive, a Zip drive that burns a CD-ROM), then it's better to make a copy on it. Question :When launched, the program does not load and displays the message "Protection key not found". Answer: This error can occur due to a number of reasons. Solutions depend on whether you have a network version or a local one. Let's start with the local one, as with a simpler case. We suggest that you perform the following steps. After each attempt, please try to run 1C:Enterprise. It is possible that the problem will be solved at the first step, and then all subsequent ones will not be needed. a)Restart your computer by clicking Start->Shutdown ->Restart Computer ->OK. Wait until the computer restarts, then try starting 1C again. b)You may have forgotten to install the protection driver when installing the program. Then you need to run it by clicking Start ->Programs->1C: Enterprise 7.7->Install protection driver. Restart your computer and try to run 1C: Enterprise again. cCheck the physical presence of the key on the computer, maybe someone touched it and it fell out of the computer. To do this, you need to get to the back wall of the computer case, where the wires are connected. Important: It is highly recommended that you first turn off your computer. The key looks like a bar about 3x4x1 cm. Most likely, it will be red or white. The key is inserted into the LPT port (the same place as the printer). In any case, you will only be able to insert the key into the LPT port. Important: no need to exert great force, the effort should be comparable to the effort when raising a glass of tea. If the key does not fit into the port, do not try to force it in, as either it is not a key or you are not inserting it into the LPT port. It is better to call the person responsible for computers in your company, or call us. After you have inserted the key into the port, turn on the computer and try to start 1C: Enterprise again. d)Sometimes a printer and other equipment installed "on top" of a key can interfere with its determination by the protection server. Having previously turned off the computer and the printer, try disconnecting the peripherals (most often the printer) from the computer, leaving the key in place. Now turn on the computer and try to start 1C. Of course, in this case, you will not be able to use the disabled device. If you are using the network version, and the key is not located on your computer, it is recommended that you contact the person who is responsible for the operation of computers in your company for help. If you are this person, then we can advise you to do the following: a) Check that the problem computer "sees" the server where the key is located. You can either ping the server from the command line by running the ping program from the problem computer with the server computer name as a parameter. For example, c:ping server1c. Or you can simply check the presence of the server computer in the list of computers available to the client by clicking on the "My Network Places" icon. If it turns out that the problem computer does not "see" the server, then you will need to conduct a standard check for network problems. We recommend starting by checking the integrity of the cables (there are no breaks), the health of the hub, the health of the network card (is the light on, is the ping 127.0.0.1 command successful), in addition, you should make sure that the necessary protocols are available and that they are configured correctly. b)Make sure that the "Protection Server" program is running on the computer with the dongle. This program is necessary for the work of 1C: Enterprise clients in the network version. You can run it by clicking Start ->Programs->1C:Enterprise 7.7->Protection Server. c) On each computer with 1C: Enterprise there is a nethasp.ini file, which by default is located in C: Program Files1Cv77BIN. This file contains settings for the program that checks for the presence of a key on the network. The file is well documented and you can probably understand its structure. We recommend that you pay special attention to the lines of the protocols used (perhaps there is one IPX / SPX left that is not used at all in your network), the key search waiting time (in case of a weak network, the program may simply not have time to find it) and links to the server computer (perhaps the computer no longer exists, has been moved or renamed). Question: When you start 1C: Enterprise, the program does not load and displays a message like "The database directory was not found C: 1C." Answer: This happened due to the fact that the folder in which the 1C base is located is not available. If the database is located on your computer, then most likely you have moved it somewhere. Remember if you have moved any directories (folders) recently. If you know exactly where the base was moved, or it seems to you that the recently moved folder is the base, then when starting 1C, select the “Change” button in the dialog box (on the right are the OK, Cancel and next buttons - “Change”). Specify a new path to the database and, by clicking on the OK button, start 1C: Enterprise again. If the database is not on your computer, but on a remote server, then it is better to ask for help from the person who is responsible for the performance of computers in your company. If you still decide to fix the problem yourself, then, firstly, you need to check the existence of a network between the two computers (you can simply check the presence of the server computer in the list of computers available to the client by clicking on the "My Network Places" icon). Secondly, you need to find out the location of the directory with the database on the server. After that, by clicking on the "Change" button in the 1C: Enterprise launch dialog box, select "My network environment" -> Server on which the database is located -> Specify the path to the database. Now try running 1C: Enterprise again. Question: I can’t start 1C: Enterprise, the program stops with the error “Data blocking error. Perhaps the data is being used by another task." Answer: 1C: An enterprise can be launched in two modes: Exclusive and Divided. In exclusive mode, only one user can open the database. The above message indicates that someone is already logged in in exclusive mode (perhaps you), and now you are trying to use the database. The first thing to do is to check your computer. Look at the taskbar (to the right of the "Start" button), if you see the inscription "1C: Enterprise" there, then click on it and close it. It was a previously launched copy of the 1C: Enterprise program. Run 1C: Enterprise again. If 1C: Enterprise in exclusive mode is not running on your computer, then two options are possible. The first option is applicable if there are few computers on the network using 1C: Enterprise, and they are located close to each other. Then you can go to each computer and, by selecting the menu item 1C: Enterprise Help -> About the program, you will see the Mode of operation in the very last line. If “Exclusive” is written on the left, then you need to close 1C: Enterprise on this computer and run it on your own. Most likely, the problem will be solved. The second option should be used when there are a lot of computers on the network, and it takes too long to bypass them one by one. Then you need to start the Monitor with the Start -> Programs -> 1C: Enterprise -> User Monitor command. After starting the monitor, you need to select the menu item Monitor -> Active users. You will see a list of computers from which the database is currently being used (each line is a running 1C component: Configurator, Enterprise, Monitor, Debugger). If you pay attention to the leftmost column, you may notice that one of the computers is running 1C: Enterprise in exclusive mode (this is indicated by a red exclamation mark next to the icon). Go to this computer and close 1C: Enterprise there. The problem should now be solved. Sometimes it is possible that some computer has incorrectly shut down (or simply “frozen”), then you need to turn it off and turn it on again. If it is impossible to determine which computer occupied the base, and the Monitor does not specify a computer using the exclusive mode, then you will have to turn off all computers (you can do it one by one, trying to start 1C after turning off each computer). Question: The program does not start and displays the message "Error loading metadata". Answer: There is no general solution to the problem here. First, make sure that the correct database path is specified. You can check this by looking at the inscription at the very bottom of the 1C: Enterprise launch window. The path to the database should appear there (something like C: 1C). If you don’t know if this path is the right one, then read the answer to the question “When starting 1C: Enterprise, the program does not load and displays a message like “The base directory was not found C: 1C”. If this does not help, then try contacting the person in charge of computers in your company. If you have no one to turn to or it turns out that the path is correct, but the database, nevertheless, does not start, then it is better to contact us. Question: The program does not start and displays the message "Error opening table index file. To restore index files, run the program in exclusive mode." Answer: To solve this problem, you need to run the program in exclusive mode (check the "Exclusive" box when starting the program). Of course, you will first have to ask all users to exit 1C: Enterprise. The offer to restore index files must be answered in the affirmative. This process can take a significant amount of time, from 1-2 minutes for databases of 5-10 megabytes to about an hour for large databases. If you are unable to start the system in exclusive mode, although you are sure that all users have exited the program, then first check your computer, perhaps there is still a running copy of the program. If this did not help, then try turning off the client machines (you can do it one by one, with a check after each). It is likely that one of the programs was incorrectly terminated and did not release the database. Question: The program does not start and displays the message "The log file is corrupted." Answer: In your base directory (the path to the base is written at the bottom left in the launch window) there is a Syslog subdirectory. This directory contains the 1cv7.mlg file, this is the log file. Move it to another directory; if you think you don't need the log file, you can delete it. The main thing is to remove the log file from this directory. The next time you start 1C:Enterprise, it should successfully boot up and create an empty log file. Question: When you start the program, a pop-up screen appears with the inscription 1C: Enterprise and immediately disappears. Answer: This problem arose due to the fact that you are not allowed to write to the database directory. 1C:Enterprise to run requires an entry in this directory. To correct the situation from the server on which the database is located, select the share (disk or directory with the database), right-click, select the Properties menu, the Access tab, set the value to Full (or rearrange the indicator to "Share the folder" for Windows 2000). Save the changes, try running 1C: Enterprise again. Question: When trying to open a database, the program stops with an error message: "The sort order set for the database does not match the system sort order." Answer: To fix this error, click on the icon My Computer-> Control Panel-> Languages and Standards. Set the suggested value to "Russian" and restart your computer. Question: When starting the program, the download stops with an error message: "Runtime Error! Program c:Program Files1Cv77Bin1Cv77.exe. Abnormal Termination". Answer: There may be several reasons for this error to occur. First, copy your base directory to another location so that even in the worst case scenario (the lights were turned off during the fix), you can return to the situation before the start of the fix. You can take the following steps to fix this error yourself. After each step, try to start 1C: Enterprise.
- Restart your computer.
- Reinstall 1C: Enterprise.
- Copy the file 1Cv7.md, which is located in the NEW_STRU directory of your base, to your base directory. For example, if your base is located in the c:1Cbase directory, then you need to copy the 1Cv7.md file from c:1CbaseNEW_STRU to c:1Cbase. To the question: "Should I replace the current file?" should answer "Yes".
- Run the Configurator, select Administration -> IS testing and fixing. Click the Run button.
1cv7.exe MODE [ /M | /D | /u | /n | /P],
where MODE - startup mode, can take only one of three values:
config - configurator mode;
debug - debugger mode;
enterprise - normal (working) mode 1C: Enterprise.
the following keys are optional:
/M - run the program in exclusive mode;
/D - database directory;
/U - user's working directory (the directory from the list of users is ignored);
/N - username;
/P - user password;
/T - path to temporary files
/@ - for the configurator mode, specifying the batch file
/W - Web extension initialization
Example: 1cv7 enterprise /Dc:1cmainbase /NIvanov /P123,
in this case, the program will start without displaying dialogs about choosing a base and operating mode, and also without prompting for a user name and password.
Running in batch mode is described in detail in the book “Configuration and Administration. Part Two" on page 252.






The printer does not print and is not available - what to do
The best android emulators for pc The best game console emulators for windows
What is the .odt file extension?
Clipboard operations in puTTY Putty paste from clipboard
How to make a folder icon (icon) from your photo How can I change the shortcut icon